Field Mappings & Custom Properties
Configure how HubSpot fields map to Quotient fields and work with custom properties
Overview
Field mappings control how data flows between HubSpot and Quotient, ensuring that information is correctly synchronized between the two systems. Quotient uses a sophisticated two-phase transformation system that combines built-in mappings for critical fields with user-configurable mappings for custom business needs.
How Field Mappings Work
Two-Phase Transformation System
Quotient processes HubSpot data through two distinct phases:
Phase 1: Built-in Transformations
- Non-configurable logic for critical and complex fields
- Handles essential data like email addresses, IDs, and relationships
- Manages complex transformations like address parsing and revenue calculations
Phase 2: Configurable Mappings
- User-customizable mappings for standard and custom fields
- Default mappings provided for common HubSpot properties
- Support for custom properties and business-specific fields
This approach ensures data integrity for critical fields while providing flexibility for your unique business requirements.
Default Field Mappings
Quotient provides sensible default mappings for common HubSpot properties. These can be customized to match your specific needs.
Contact (HubSpot) → Person (Quotient)
| HubSpot Field | Quotient Field | Type | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| emailAddress | Built-in | Bi-directional | |
| firstname | firstName | Default | Inbound |
| lastname | lastName | Default | Inbound |
| jobtitle | jobTitle | Default | Inbound |
| phone | mainPhoneNumber | Default | Inbound |
| department | department | Default | Inbound |
Company (HubSpot) → Company (Quotient)
| HubSpot Field | Quotient Field | Type | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | name | Built-in + Default | Bi-directional |
| description | description | Default | Inbound |
| industry | industry | Built-in + Default | Inbound |
| website | website | Default | Inbound |
| phone | phoneNumber | Default | Inbound |
| annualrevenue | revenue | Built-in | Inbound |
| numberofemployees | totalEmployees | Built-in | Inbound |
Built-in vs Default Mappings
Built-in mappings handle critical fields and complex transformations that ensure data integrity. Default mappings are user-configurable and can be modified to match your business needs.
Built-in Transformations
These transformations are automatically applied and cannot be modified to ensure data integrity:
Contact Built-ins
emailAddress: Critical for person identification and deduplicationhubspotId: Maintains sync relationship between systemssource: Automatically set to "HUBSPOT" for trackingassociatedCompanyHubspotIds: Preserves company relationships- Email Marketing Defaults: New contacts default to "NOT_SUBSCRIBED"
Company Built-ins
- Address Parsing: HubSpot's combined address fields are decomposed into:
address(street address)citystatezipcountry
- Revenue Processing: Handles currency conversion and formatting
- Industry Arrays: Converts HubSpot industry strings to Quotient arrays
- Social Media Links: Extracts and formats social media URLs
Deal Built-ins
- Pipeline Mapping: Preserves HubSpot pipeline and stage information
- Amount Formatting: Handles currency and decimal formatting
- Date Processing: Converts HubSpot date formats to Quotient standards
Custom Properties
Creating Custom Properties in HubSpot
Before mapping custom properties, ensure they exist in HubSpot:
- In HubSpot, go to Settings → Properties
- Select the object type (Contacts, Companies, or Deals)
- Create a new property with these considerations:
- Choose an appropriate field type (text, number, date, etc.)
- Set a clear internal name (this will be used in mappings)
- Configure field options if using dropdowns or checkboxes
Supported Property Types
Quotient supports all HubSpot property types with automatic data conversion:
| HubSpot Type | Quotient Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Single-line text | STRING | Direct mapping |
| Multi-line text | STRING | Preserves line breaks |
| Number | NUMBER | Handles decimals and integers |
| Date picker | DATE | Date only, no time |
| Date & time picker | DATETIME | Full timestamp with timezone |
| Dropdown select | SINGLE_SELECT | Maps option values, single choice |
| Multiple checkboxes | MULTI_SELECT | Multiple values from predefined options |
| Multi-line text (as list) | LIST | Flexible text list, line-separated |
| Radio select | ENUM | Single value selection |
| Yes/No | BOOLEAN | True/false values |
| HubSpot user | USER | Maps to Quotient users |
Mapping Custom Properties
To create a custom field mapping:
- Navigate to HubSpot integration settings
- Go to Field Mappings section
- Click "Add Field Mapping"
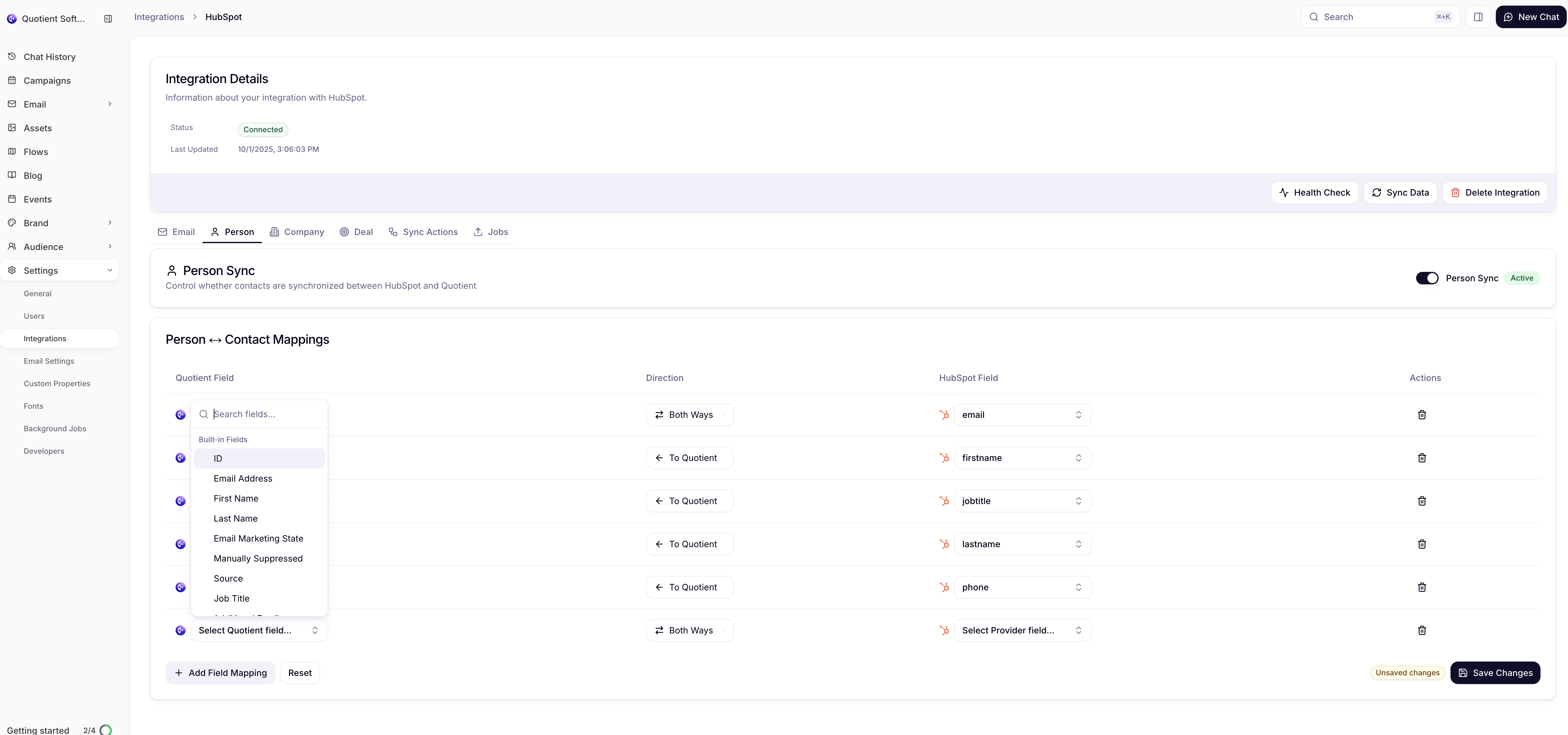
- Select the HubSpot Field: Choose from available HubSpot properties
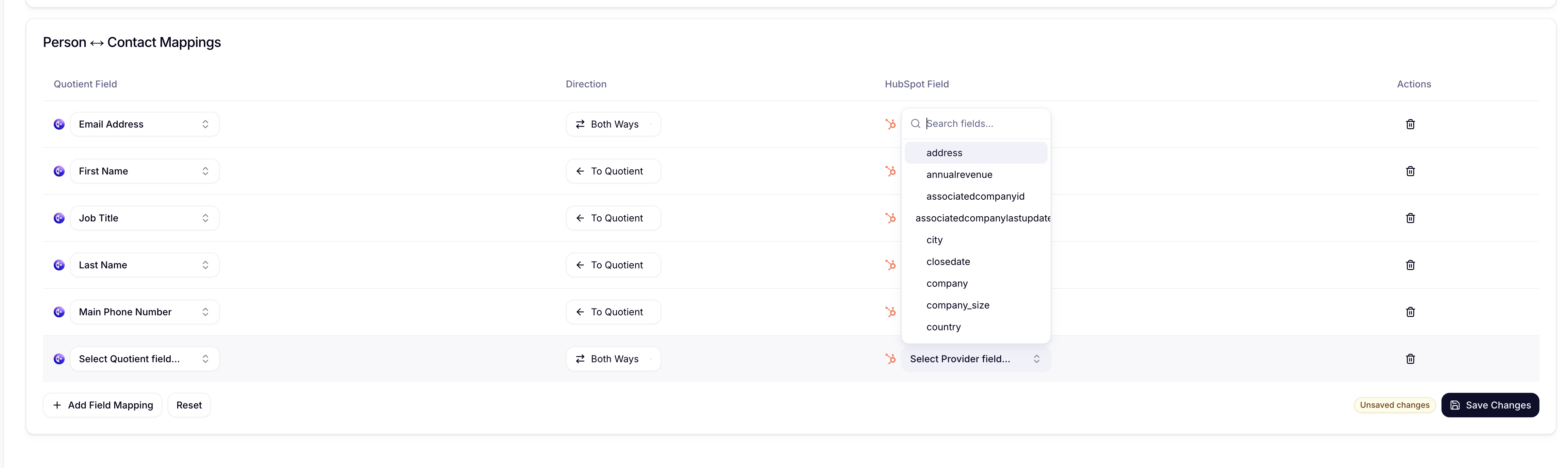
- Configure the mapping:
- Quotient Field: Choose existing field or create new custom property
- Data Type: Automatically detected but can be overridden
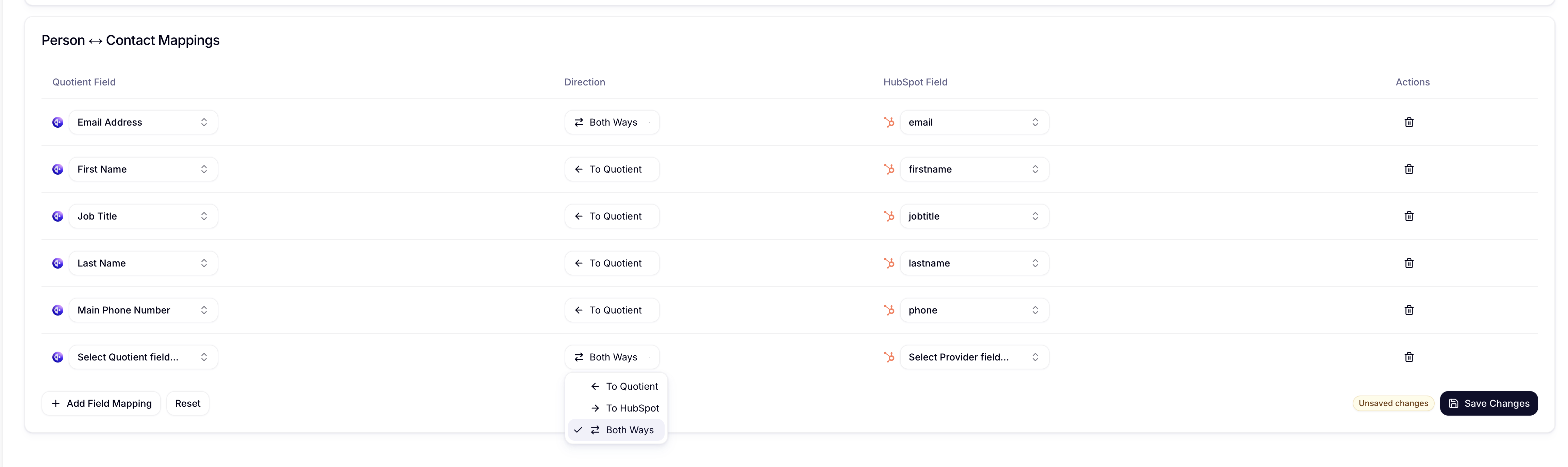
- Sync Direction: Choose Inbound, Outbound, or Bi-directional
Example: Custom Lead Score Mapping
Let's say you have a custom "Lead Score" property in HubSpot that you want to sync to Quotient:
HubSpot Setup:
- Property name:
lead_score - Type: Number
- Used for: Lead qualification scoring
Quotient Mapping:
- HubSpot Field:
lead_score - Quotient Field:
leadScore(custom property) - Data Type:
NUMBER - Direction:
INBOUND(HubSpot is the source of truth)
Advanced Mapping Scenarios
Handling Enumeration Fields
For HubSpot dropdown and checkbox properties:
HubSpot Options:
- Option 1: "Enterprise"
- Option 2: "Mid-Market"
- Option 3: "SMB"
Quotient Mapping:
- Values are mapped exactly as they appear in HubSpot
- Multiple selections are joined with semicolons
- Empty selections map to null values
Date and Time Handling
Date Fields:
- HubSpot date-only fields map to Quotient
DATEtype - Time information is ignored for date-only fields
- Timezone is preserved for datetime fields
DateTime Fields:
- Full timestamp with timezone information
- Automatic conversion between HubSpot and Quotient formats
- Handles daylight saving time transitions
User and Owner Mappings
HubSpot Owner Fields:
hubspot_owner_idmaps to Quotient user assignments- Requires users to exist in both systems
- Falls back to null if user mapping not found
Managing Field Mappings
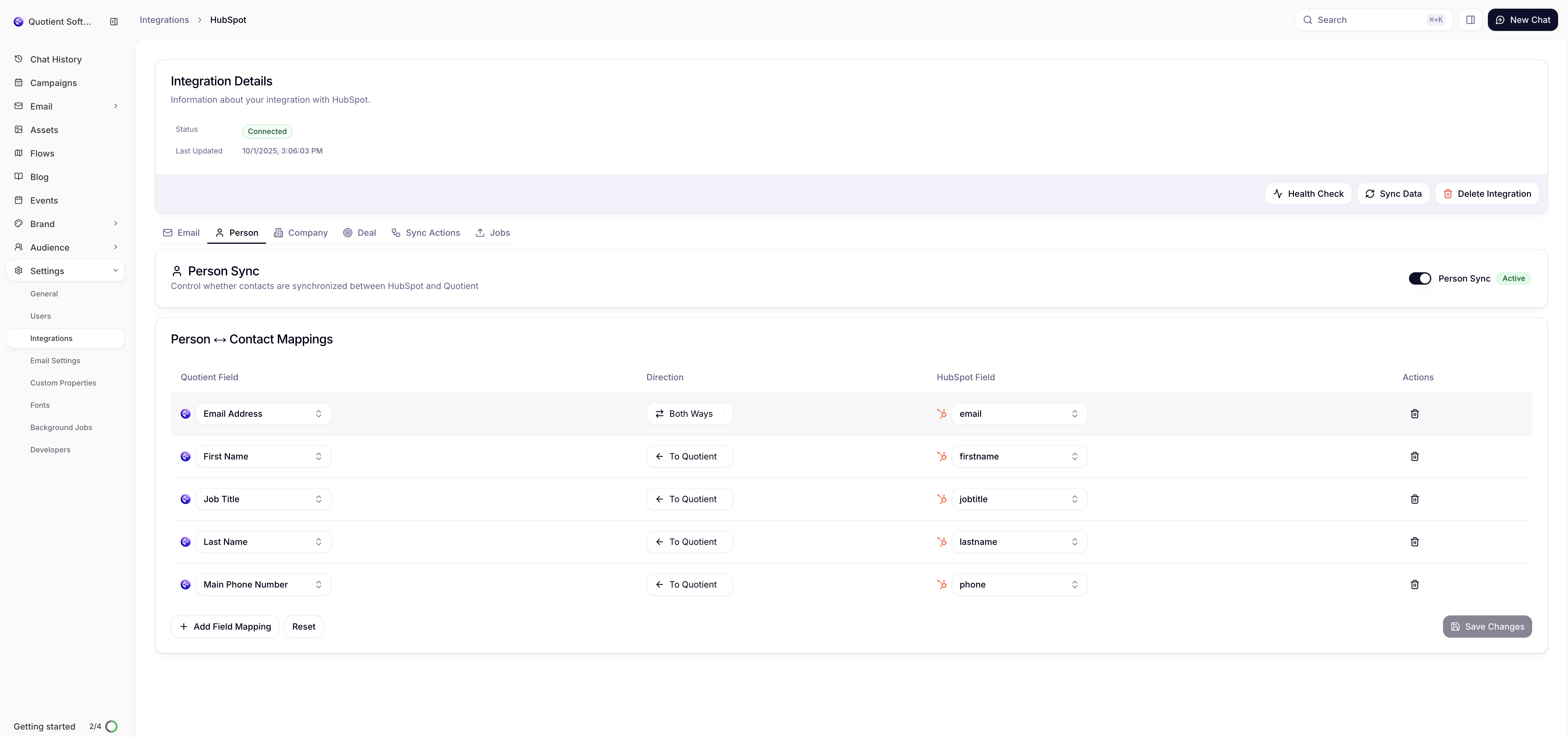
Viewing Current Mappings
In the HubSpot integration settings:
- Default Mappings: Pre-configured mappings for standard fields
- Custom Mappings: Your business-specific field mappings
- System Mappings: Built-in mappings that cannot be modified
Modifying Mappings
To Edit a Mapping:
- Find the mapping in the Field Mappings section
- Click the edit icon
- Modify the configuration
- Save changes (triggers a sync for affected records)
To Delete a Mapping:
- Click the delete icon next to the mapping
- Confirm the deletion
- Data previously synced through this mapping remains unchanged
Testing Mappings
Field Mapping Validation:
- Test mappings with sample data before full deployment
- Use the "Test Sync" feature for individual records
- Monitor sync logs for mapping errors or data type issues
Troubleshooting Field Mappings
Common Issues
Data Not Syncing
- Verify the field exists in both HubSpot and Quotient
- Check that data types are compatible
- Ensure the mapping direction allows the desired data flow
Data Type Errors
- Review HubSpot property type vs Quotient field type
- Check for invalid data in source fields (e.g., text in number fields)
- Verify enumeration options match between systems
Missing Custom Properties
- Ensure custom properties are created in HubSpot first
- Check property permissions and visibility settings
- Verify the property is associated with the correct object type
Best Practices
Naming Conventions
- Use consistent naming between HubSpot and Quotient
- Avoid special characters in custom property names
- Use descriptive names that indicate the field's purpose
Data Type Selection
- Choose the most restrictive appropriate data type
- Use
ENUMfor fields with limited, known values - Use
STRINGfor flexible text fields
Sync Direction Strategy
- Use
INBOUNDwhen HubSpot is the authoritative source - Use
OUTBOUNDwhen Quotient generates the data - Use
BIDIRECTIONALcarefully to avoid sync conflicts
Read-Only Properties
When syncing data from HubSpot, you may want to mark certain Quotient properties as read-only. This prevents users from editing these values in Quotient since HubSpot is the source of truth.
When to use read-only properties:
- Inbound-only sync: Data flows from HubSpot to Quotient but not back
- CRM-managed fields: Values that should only be updated in HubSpot
- Calculated fields: Scores or metrics computed in HubSpot
- Compliance data: Information that requires CRM approval to change
Setting up read-only properties:
- When creating or editing a custom property in Quotient, check the "Read-only" checkbox
- Read-only properties can still be used for segmentation and email personalization
- Users will see these values but cannot edit them in forms or preference pages
Example use cases:
- Lead scores calculated by HubSpot workflows
- Company industry classifications from HubSpot
- Deal stages and pipeline information
- Compliance flags or certification statuses
Next Steps
Once you've configured field mappings:
- Set Up List Synchronization - Configure list and segment sync
- Enable Email Sync - Sync email templates and broadcasts
- Monitor Sync Performance - Track and optimize sync operations
HubSpot Help Resources:
- HubSpot Properties Guide - How to create and manage properties
- Custom Properties in HubSpot - Step-by-step property creation
- HubSpot CRM Setup - General CRM configuration help